So far, we have been exploring a 1-dimensional “space” of points along an infinitesimally thin line. Mathematicians call this a 1-dimentional space. The concept of symmetry implies that the line looks exactly the same in both directions. Therefore, this line must extend on forever in both directions, there is no point on the line where it ends. The line looks exactly the same on both sides of every point.
The concept of point symmetry in 1-dimensional space also means that if you were to reverse the direction of the “ruler” that measures the distance between any two points in this space, you will still measure the same distance between the points. This concept of invariance of direction is one of the most important characteristics of space. Of course, we need a lot more than just one line to describe all the space around us.
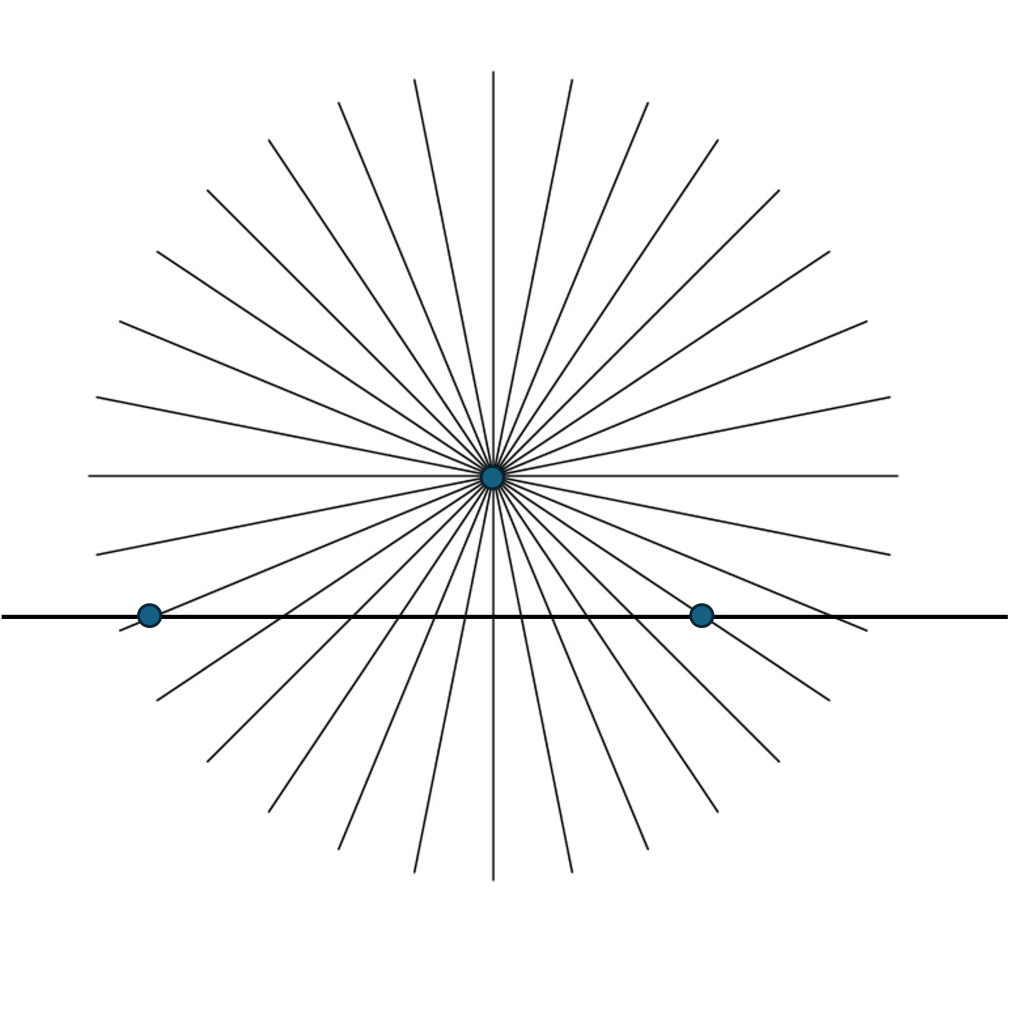
In order to expand the dimensions of space beyond this 1-dimensional space, we must assume that there is some point that is not in this space, a point that is not on the line. When we find a point that is not on the line, we can create a new line between any point on the line and the new point. This defines a new 1-dimensional space (a line) for every point on the original line, all of these new lines pass through the new point.
Since there are an infinite number of points on the original line, we see that there are an infinite number of 1-dimensional lines that can be drawn through the new point all in different directions. The space formed by this infinite number of lines is called a 2-dimensional space. It is called 2-dimensional due to the “language” necessary to describe the location of any point in this space. To locate any point, we must choose a reference point, then first (1) we need to choose one of the lines passing through the reference point, and second (2) we use the methods we have already discussed to determine the location of a point along this reference line. Thus, the location of a point thus requires 2 numbers, one (1) to locate the reference line, and the other (2) to determine the location of the point along this line.
The concept of point symmetry in 2-dimensional spaces also comes into play. It means that measuring distances is the same in every direction. This invariance of direction means that if we have a “ruler” that measures a distance along any of the lines in this space, and we change the direction of the ruler, the length of the ruler does not change.
Imagine how the world would look if measuring lengths in one direction were different than lengths in another direction. If the invariance of direction was not true, then when we changed direction, the distance between things would shorten or lengthen, depending on which direction we faced. This is not what we experience in real life.
We can use the same concepts that we used to extend 1-dimensional space to 2-dimensional space to extend into spaces into any number of dimensions. How many distinct points do you need to generate a 3-dimensional space? Think about it. We will discuss how it can be done later.
